Internet Crime: The Simple Truth
Relevant Links:
Internet Crime: Fraud
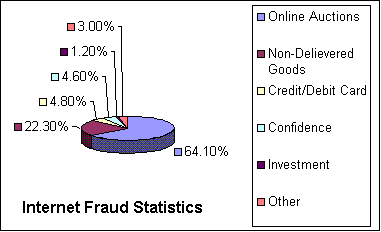
The FBI's Internet Fraud Complaint Center receives more complaints about possible online auction frauds than all other types of complaints combined. This doesn't mean that actual crimes have been committed. It only means that the majority of complaints received have involved online auctions. Further study reveals that less than 1% of online auction transactions result in fraud. Yet, how meaningful are these statistics?
The vast majority of Internet Crimes go unreported or undetected. And, there is a lack of valid and meaningful Internet Crime statistics. A lack of standard definitions also adds to the confusion. However, the Internet Fraud Complaint Center has come up with the following Internet fraud categories listed below:
- Financial Institution Fraud- Knowing misrepresentation of the truth or concealment of a material fact by a person to induce a business, organization, or other entity that manages money, credit, or capital to perform a fraudulent activity. Credit/debit card fraud is an example of financial institution fraud that ranks among the most commonly reported offenses to the IFCC.
- Gaming Fraud- To risk something of value, especially money, for a chance to win a prize when there is a misrepresentation of the odds or events. Sports tampering and claiming false bets are two examples of gaming fraud.
- Communications Fraud- A fraudulent act or process in which information is exchanged using different forms of media. Thefts of wireless, satellite, or landline services are examples of communications fraud.
- Utility Fraud- When an individual or company misrepresents or knowingly intends to harm by defrauding a government regulated entity that performs an essential public service, such as the supply of water or electrical services.
- Insurance Fraud- A misrepresentation by the provider or the insured in the indemnity against loss. Insurance fraud includes the “padding” or inflating of actual claims, misrepresenting facts on an insurance application, submitting claims for injuries or damage that never occurred, and “staging” accidents.
- Government Fraud- A knowing misrepresentation of the truth, or concealment of a material fact to induce the government to act to its own detriment. Examples of government fraud include tax evasion, welfare fraud, and counterfeit currency.
- Investment Fraud- Deceptive practices involving the use of capital to create more money, either through income-producing vehicles or through more risk-oriented ventures designed to result in capital gains. Ponzi/Pyramid schemes and market manipulation are two types of investment fraud.
- Business Fraud- When a corporation, or business knowingly misrepresents the truth or conceals a material fact. Examples of business fraud include bankruptcy fraud and copyright infringement.
Fraud
is more likely to affect an individual than a company. And fraud is more
likely to be performed by an individual than a company. With a little
common sense, most Internet fraud can be avoided. I have provided several
links on the left-hand side of the screen that provide information on how
not to be victimized as well as information about common frauds currently
going around.
AAFTEC
BBB - Shopping Safety
Online
Dot Cons
(FTC)
E-Commerce
News: Study: Fraud No Threat to E-Commerce
Econsumer.gov
Internet Fraud Complaint
Center (FBI)
Internet ScamBusters
The Internet and
On-Line Trading (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission)
Copyright @ 2002 by Robert J. Trader, University of
Kentucky Graduate Student.
All rights reserved.
This page was last modified: